Opera producer/conductor Sarah Caldwell as Greek tragedy
By Peter Alexander June 11 at 10:15 p.m.
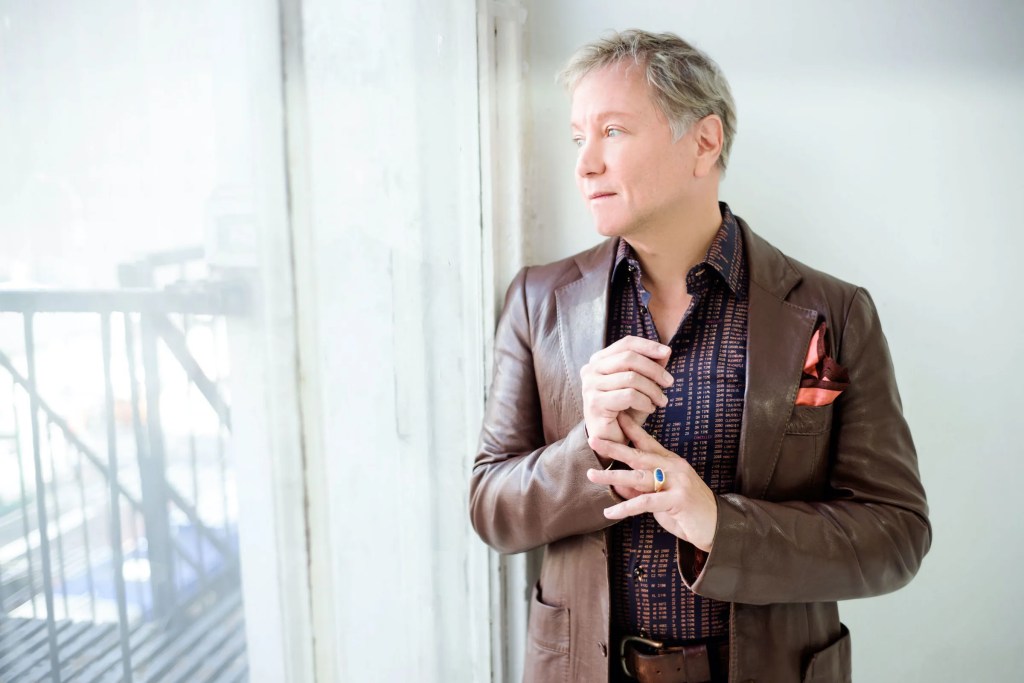
Mark Adamo knows his Greek mythology.
The composer/librettist is known not only for having written an opera on Aristophanes’s Lysistrata, but also having linked Bram Stoker’s Dracula with the Greek myth of the Bacchae as librettist for John Corigliano’s 2021 opera The Lord of Cries. And now Adamo is in Boulder workshopping his opera-in-progress Sarah in the Theater at the University of Colorado New Opera Workshop (CU NOW).
And once again he has found a Greek connection. “This is what happens when you give a 10-year-old Greek mythology to read,” he says.
With the first act mostly done, Adamo’s new opera about the opera conducting and producing legend Sarah Caldwell will have semi-staged workshop performances of excerpts this weekend (Friday and Sunday, June 13 and 15; details below). Nick Carthy, music director of the CU Eklund Opera Program will conduct. The performance will cover the first act, but “there will be a surprise,” Adamo says cryptically.
Adamo discovered a parallel between Caldwell’s career and a Greek myth when he first undertook work on the opera. “As I’m sketching out (the opera), I had a sense of what I wanted to do with her as a character,” he says. “I’m asking the question, is there some kind of narrative template that’s going to make sense of the themes in her character, which is that she’s extremely ambitious but she doesn’t see limits. Whatever happens in the theatre is the only thing that matters.
“(I thought) there has to be some kind of pre-existing trope that I can pull from. I don’t know—Icarus! I said, that’s it!”
In the opera, the story of Icarus, who flew too close to the sun and fell to his death, is the subject of an opera within the the opera. It becomes both an opera that Caldwell is rehearsing, revealing her relentlessly focused work ethic, and a symbol of her own high-flying career and ultimate crash.
Caldwell founded the Boston Opera Group, which became the Opera Company of Boston. Against all odds and considerable financial difficulties, she presented a wide range of operas and developed a reputation for producing remarkable results with limited means. Because of her intense focus on her work, she was known both for attracting ardent admirers and for driving others away under duress.
A synopsis of the opera released by the commissioning organization, Odyssey Opera, states: “Over one sleepless day and night: haunting the theater she created, made legendary, and now, by morning, may lose; the director, conductor, and impresario Sarah Caldwell—brilliant, obsessed, intractable—inspires her artists, fends off creditors, relives her triumphs, and battles with ghosts as we wait to learn if she will be given one final chance to continue the work she lives for or whether demons of self-sabotage have, at last, outrun her luck.”
Adamo is returning to Boulder for his second workshop with CU NOW, following a successful reworking of his opera The Gospel of Mary Magdalen in 2017. “(CU NOW) is the perfect balance of seriousness about the work, and un-seriousness about ego,” Adamo says.
“Nick (Carthy) and our pianists know it cold, but part of the point of the workshop is that you want the flexibility to change things. The magic here is that people came in with a base knowledge of the score, and also not only the ability but the imagination to get it better. I am ‘directing’ this, (but) in real life this is a co-production of me and the singers. Half the ideas on the stage will come from them.”
For all of her impact in the opera world Caldwell might not occur to most composers as the subject of an opera. The original idea came from Gil Rose, conductor of the Boston Modern Orchestra Project and founder of Odyssey Opera, who commissioned Sarah in the Theatre. But make no mistake, Adamo sees her as a great subject for drama. “She’s like Orson Wells,” he says. “It’s a race between the genius and the demons.”
Taking on the roles of both librettist and composer might seem dangerous, because the history of opera is littered with legendary battles between composers and librettists. Adamo sidesteps any conflict between the two parts of his creative mind by starting with an outline of the various characters’ motives and the emotional arc of the story. The emotional development suggests in turn the musical demands of the finished piece.
“By the time you do the first draft of the libretto, it’s coming to the first draft of the score, because you’ve got these musical requirements that you’re trying to write around,” he says. “And then by the time you get to that libretto and by the time you’re setting it, ideally you avoid the composer-librettist clash, because the composer has been there from the beginning.”
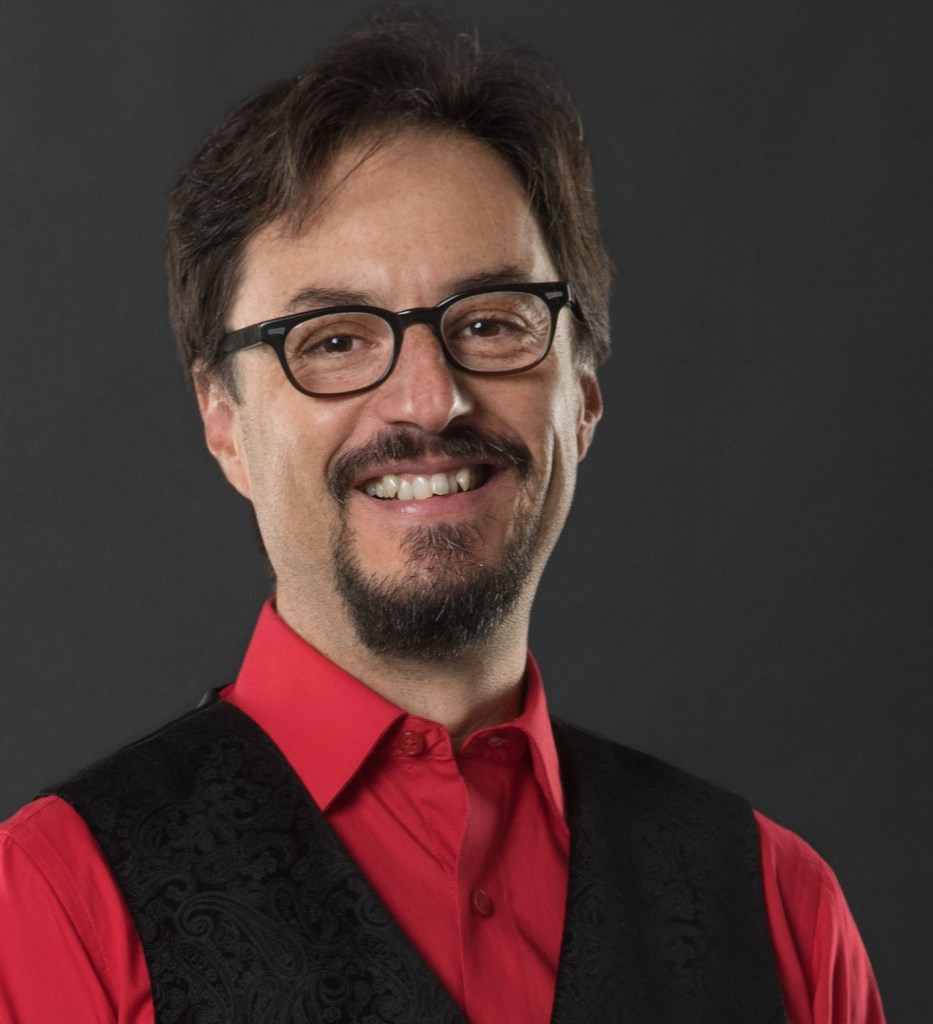
The final word on any new opera belongs to the performers who bring it to life. After several weeks of intensive work, Carthy knows where he stands on Sarah in the Theatre. “It’s a great work,” he says.
“It’s really a greek tragedy.”
# # # # #
CU New Opera Workshop (CU NOW)
Nick Carthy, conductor
Mark Adamo: Sarah in the Theatre (Act I excerpts with two pianos)
7:30 p.m. Friday, June 13 and 2 p.m. Sunday, June 15
Music Theatre, Imig Music Building
Free