Peter Oudjian to conduct famous last symphonies by Beethoven and Mahler
By Peter Alexander July 26 at 5:00 p.m.
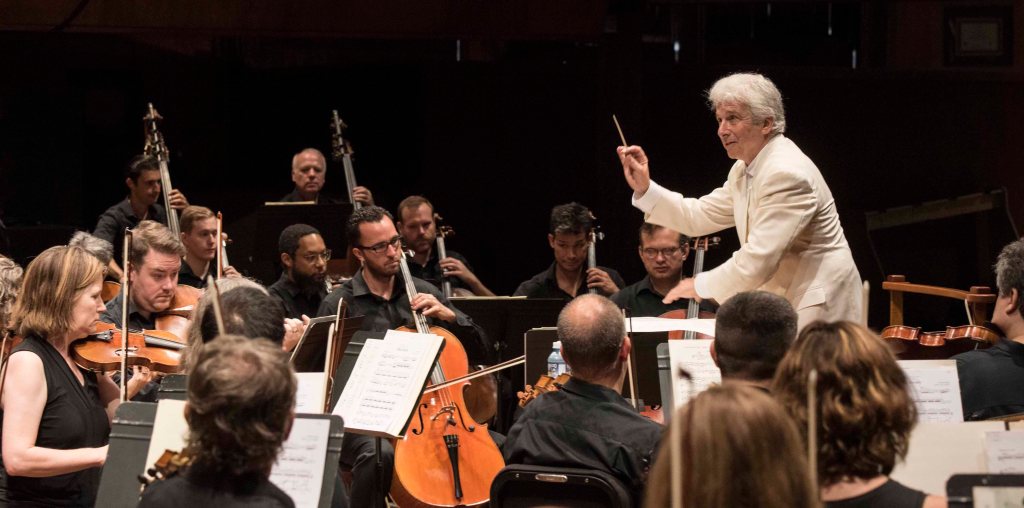
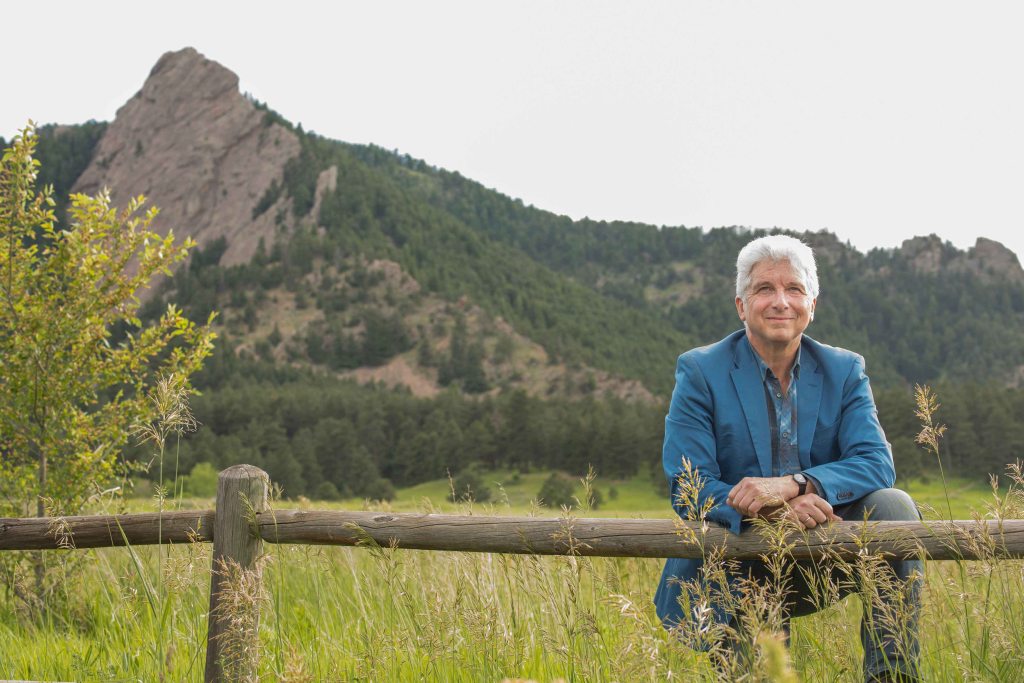
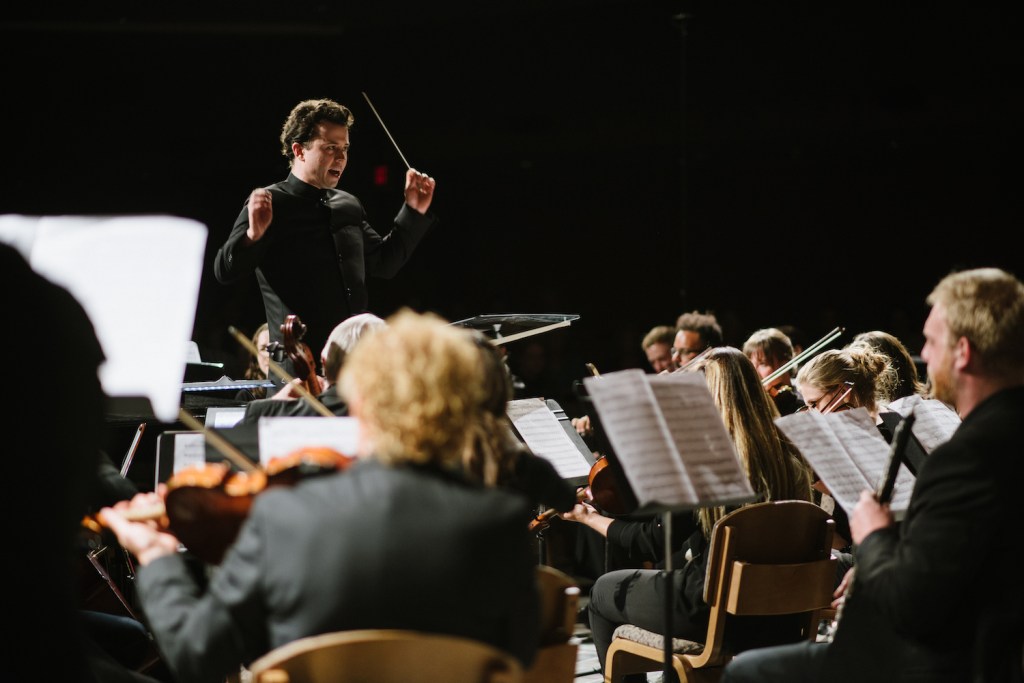
Music director Peter Oundjian will conclude the 49th Colorado Music Festival (CMF) this week with performances of two very different ninth symphonies.
Thursday and Friday will see performances of one of the most famous symphonies ever written, Beethoven’s Symphony No. 9 in D minor for full orchestra, chorus and soloists (7:30 p.m. July 31 and 6:30 p.m. Aug. 1; full programs below). Two shorter works will fill out the program both evenings: Amplify, a short work for orchestra co-commissioned by CMF from composer Michael Abels; and Beethoven’s Elegischer Gesang (Elegiac song), op.118, for string quartet and vocal quartet.
The Sunday concert will feature a much less frequently performed Ninth Symphony, that of Gustav Mahler. At 87-plus minutes, the symphony stands alone on the program. “Mahler 9 is just enough of an experience for a listener, or for that matter for an orchestra or even for a conductor,” Oundjian says. “I have done it with other pieces, but I think it’s better just to say, ‘here’s an epic thing.’ It’s more than fulfilling by any measure.”
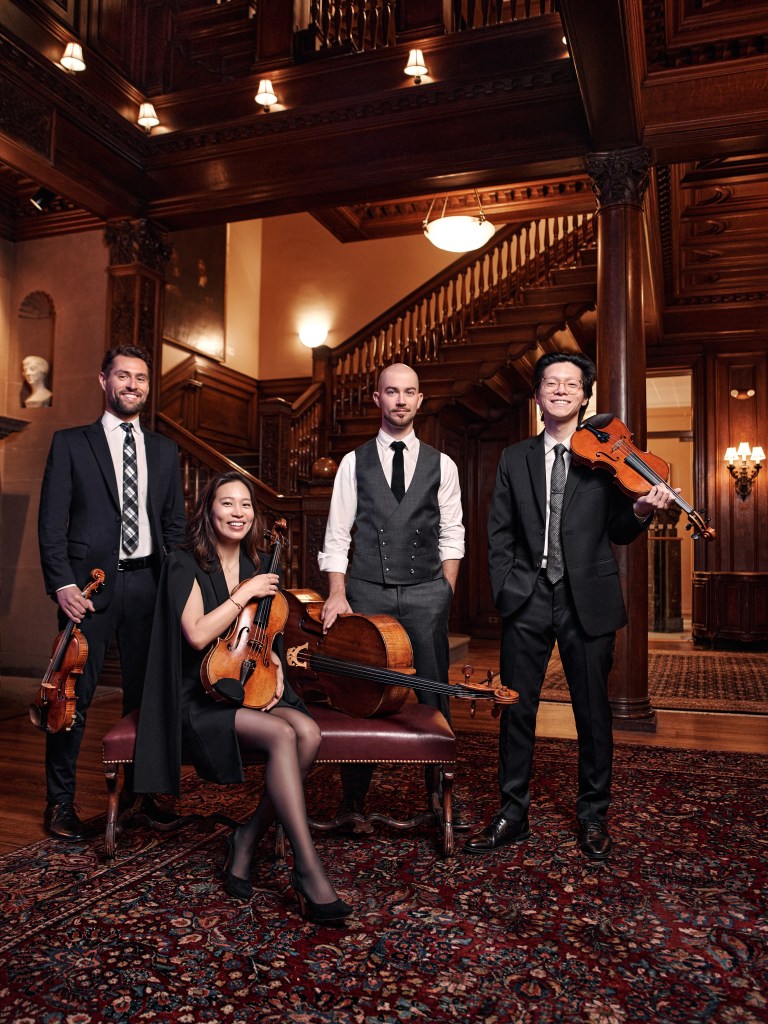
The week begins with a chamber music concert by the Dover Quartet, playing string quartets from the heart of the 19th-century to late Romantic era: music by Schumann, Tchaikovsky and Leoš Janáček. (See program below.) The Dover Quartet was formed by four students at the Curtis Institute in 2008, and is currently the Penelope P. Watkins ensemble in residence at Curtis.
The culmination of Beethoven’s career, the Ninth Symphony was first performed in May of 1824. It was a revolutionary work at the time, both for its great length and for the inclusion of voices in a symphony. When he wrote it, Beethoven was profoundly deaf, at the end of the performance the composer, who was standing onstage, had to be turned around by one of the singers so that he could see the cheering audience.

Today the Ninth Symphony has become the favorite classical piece for celebrations, largely due to its joyful finale based on Friedrich Schiller’s poem “Ode to Joy.” It was famously performed in Berlin in 1989 by Leonard Bernstein and a combined orchestra from East and West Germany to celebrate the fall of the Berlin Wall, with the word “Freude” (Joy) replaced in the text with “”Freiheit” (Freedom).
As much as he loves the entire work, Oudjian says it’s “the profundity, beauty and sense of longing that the slow movement displays” that makes the Ninth a great work. “The depth of this slow movement is for me the peak of the experience,” he says.
“This is among the greatest (musical) variations that was every written. The way he uses the skill of embellishment and transformation among the most important elements (goes) beyond what one could ever imagine.”
Due to the impact of the symphony, and the fact that long after no major composer wrote more than nine symphonies, a legend grew that there was a supernatural limit on the number of symphonies one could write. No one bought into that legend more than Mahler, who avoided as long as possible writing a Ninth symphony. In fact, after his 8th, he called his next major piece Das Lied von der Erde (The song of the earth) rather than a symphony.
Having safely completed Das Lied, Mahler went on to complete his Ninth Symphony. Ironically, it was still his last completed symphony, although his Tenth has been completed by various editors based on one mostly finished movement and sketches.
As profound as it is, Mahler’s Ninth is not played nearly as often as Beethoven’s. That may be in part because it takes such focus to shape the music over such a long span of time. For Oundjian, the key is to conceive of the performance as a journey.
“[It takes] a tremendous amount of concentration, but you never say ‘Oh my god, I’ve still got to be playing this for 25 more minutes’,” he says. “You’re just thinking about where you are in the journey, and what’s coming and how important this moment is.”
In contrast to Beethoven’s Ninth, Mahler’s Ninth is less a grand celebration and more a final reduction of the symphony into its smallest elements. “Deconstruction is exactly what happens,” Oudjian says. “You have one little gesture that lasts a few notes, then another gesture that removes a couple of notes, and finally just a cadence.”
The key to understanding the Symphony is to hear how the very contrasting movements outline the journey from start to finish. “The first movement is the greatest expression of anguish that you could imagine, but also a strange kind of optimism,” Oundjian says. “The second movement is really bizarre, looking backwards to a simpler time, the Baroque or early classical period.
“The third movement looks forward to modernism in a way that you could never imagine. It sounds like Shostakovich or Hindemith half the time—later composers (who) were very influenced by Mahler. And the final movement is a statement unlike any other. It’s about eternal beauty and longing and possibility, and perhaps the end is an image of the afterlife, or even the journey between one life and the next. But it’s staggeringly beautiful and it uses silences in a way that no composer had ever dared to do.”
And in the end, Mahler’s silences will help close the 49th Colorado Music Festival.
# # # # #
Colorado Music Festival, Peter Oundjian, music director
Tuesday, July 29–Festival Finale, Sunday, Aug. 3
All performances in Chautauqua Auditorium
Chamber Music Concert
Dover Quartet
- Leoš Janáček: String Quartet No. 1 (“Kreutzer Sonata”)
- Schumann: String Quartet No. 1 in A minor, op. 41
- Tchaikovsky: String Quartet No. 1 in D major, op. 11
7:30 p.m. Tuesday, July 29
Festival Orchestra Concert
Colorado Music Festival orchestra and the St. Martin’s Festival Singers
Peter Oundjian, conductor
With Lauren Snouffer, soprano; Abigail Nims, mezzo-soprano; Issachah Savage, tenor; and Benjamin Taylor, baritone
- Michael Abels: Amplify (CMF co-commission)
- Beethoven: Elegischer Gesang (Elegiac song), op. 118
—Symphony No. 9 in D minor, op. 125
7:30 p.m. Thursday, July 31
6:30 p.m. Friday, Aug. 1
Festival Finale
Colorado Music Festival Orchestra, Peter Oundjian, conductor
Mahler: Symphony No. 9
6:30 p.m. Sunday, Aug. 3
Remaining tickets for these performances available through the CMF Web Page.